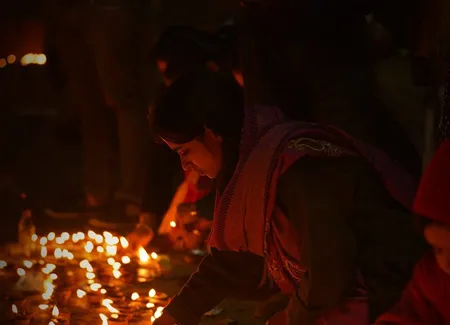
UNESCO has added Deepavali to its Intangible Cultural Heritage List, recognising it as a cultural treasure that must be preserved and celebrated
Image: IANS
Diwali or Deepavali, one of the foremost cultural and spiritual festivals celebrated by Hindus worldwide, has been included in UNESCO's Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) list.
UNESCO announced the development on its official X handle, stating: “BREAKING. New inscription on the #IntangibleHeritage List: Deepavali, #India. Congratulations!”
Randhir Jaiswal, spokesperson for the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) took to social media 'X' and said, "A joyous moment as Deepavali, the festival of lights, marking the triumph of good over evil and the return of Lord Rama to his kingdom Ayodhya, which is celebrated globally, is added to the @UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage list."
A total of 67 nominations submitted by nearly 80 countries, including India’s Deepavali festival, were examined during the week-long key session of UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, which began at Delhi’s Red Fort on Monday.
The 20th session of the Committee is being held at the iconic Mughal-era monument until Saturday.
This marks the first time India is hosting a session of the UNESCO panel.
The Red Fort has been designated as the main venue, where top dignitaries and international representatives are witnessing cultural performances, ceremonial lighting of diyas, and curated exhibitions showcasing traditional arts associated with the festival.
To ensure the city reflects the festive spirit, the Delhi government has been instructed to illuminate key buildings, install decorative lighting, place diyas across public spaces, and organise cultural programmes in various districts.
The aim is to make the national capital appear as if it is glowing in full Diwali splendour. Chhath Puja, a festival dedicated to worship the Sun God, was also nominated for UNESCO’s Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
India currently has 15 elements inscribed on UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage list, including the Kumbh Mela, Kolkata’s Durga Puja, Gujarat’s Garba, Yoga, Vedic chanting, Ramlila, Ramman, and Kutiyattam.
With Deepavali’s inclusion, India’s cultural prestige on the global stage receives a further boost. UNESCO established the Intangible Cultural Heritage List to ensure better protection of important cultural practices around the world and to create wider awareness of their significance.
The list encompasses living expressions and traditions, including skills, knowledge, expressions, representations, and practices, as well as the artefacts, objects, instruments, and cultural spaces associated with them, which communities or individuals recognise as part of their cultural heritage.